Formula 1 Race Strategy: Simulation, Setup, Prediction & Optimization
In Formula 1, races are won and lost not just on raw speed, but on strategy. From tire choices and pit stop timing to fuel management and responding to safety cars, every decision counts. Best F1 teams spend months preparing for each race, analyzing data, simulating scenarios, and planning contingencies to gain a competitive edge. In this comprehensive guide, we explore race strategy simulation, setup, prediction, optimization, mistakes, and planning — all within the context of Formula 1.
What is a Formula 1 Race Strategy?
A Formula 1 race strategy is a detailed plan used by teams to maximize their performance during a Grand Prix. It includes decisions about:
- Tire compounds and pit stop timing
- Fuel load management
- Overtaking tactics and driver instructions
- Adapting to weather changes and safety car periods
Unlike other forms of motorsport, F1 requires split-second decisions. Teams must combine real-time telemetry, predictive modeling, and driver feedback to optimize outcomes, especially during an F1 Sprint race where strategy and timing are even more critical.
Race Strategy Simulation in Formula 1
The Role of Simulation
Simulation is a cornerstone of modern F1 strategy. Teams use advanced software to predict race outcomes and test multiple scenarios without risking on-track failure. Simulations account for:
- Track layout and sector performance
- Tire degradation rates for each compound
- Weather and temperature changes
- Competitor pace and overtaking probability
- Safety car and virtual safety car interventions
Simulation allows engineers to model the entire race, identify potential risks, and determine the most effective pit stop windows. Just like teams rely on precise data for performance, ferrari F1 apparel lets fans show their support with authentic racing gear.

Simulation Benefits
- Data-Driven Decisions: Teams can base strategies on solid predictive data rather than guesswork.
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the chance of costly mistakes during the race.
- Optimal Performance: Helps select the best tire strategies and pit timing.
Tools and Technologies
F1 teams use proprietary simulators integrated with real-time telemetry. Popular tools include:
- F1 Team Strategy Software
- Live telemetry dashboards
- Predictive AI modules for pit stops and tire degradation
These systems allow teams to adjust strategies mid-race as conditions evolve, a flexibility often emphasized by Max Verstappen’s Dad.
Race Strategy Setup in Formula 1
Setting up an F1 race strategy involves several critical elements:
Tire Strategy
Tires are the most crucial element in F1 performance. Decisions include:
- Compound Selection: Soft, medium, or hard tires based on track and temperature
- Pit Stop Planning: Deciding how many stops to make and on which laps
- Tire Management: Adjusting pace to maximize tire life without losing speed
Teams also consider FIA rules, such as the mandatory use of at least two different dry compounds in a race, adding complexity to planning and strategy, reflecting the rich motorsport legacy of Formula 1.
Fuel Load Management
While modern F1 cars don’t refuel during the race, fuel load still impacts:
- Car balance and speed
- Tire degradation rates
- Pit stop timing and overall race pace
Teams calculate fuel strategies to ensure the car is fastest when it counts, without compromising safety or efficiency.
Driver Strategy and Communication
Drivers receive constant updates from race engineers about:
- Overtaking opportunities
- Tire and fuel management
- Adjustments due to competitors’ strategies
- Safety car deployment and gaps in the field
Effective communication ensures the driver can execute the strategy perfectly.
Track-Specific Strategy
Every circuit presents unique challenges. Teams analyze:
- Corner types and high-speed sections
- Historical data on tire wear and fuel consumption
- Track temperature and weather patterns
Tailoring strategies to track characteristics is essential to maximize performance, while understanding F1 overtaking rules helps drivers make the most of every opportunity on the circuit.
Race Strategy Prediction in Formula 1
What is Race Prediction?
Race prediction uses historical data, simulation, and real-time telemetry to forecast how a race will unfold. It helps teams anticipate:
- Pit stop windows
- Safety car interventions
- Competitor overtakes
- Tire degradation rates
Factors Affecting Predictions
- Sudden weather changes
- Safety car or virtual safety car periods
- Mechanical failures
- On-track incidents like crashes or penalties
AI and Machine Learning in Prediction
Top F1 teams now leverage AI and machine learning to enhance race prediction:
- Pattern Recognition: Analyzes past races to anticipate competitor behavior
- Probability Models: Calculates the likelihood of pit stop success or tire degradation
- Real-Time Support: Suggests adjustments to strategy during the race
AI predictions combined with human expertise allow teams to adapt instantly to evolving race conditions, giving drivers like Lewis Hamilton a strategic advantage on the track.

Race Strategy Optimization in Formula 1
The Goal of Optimization
Optimization ensures the chosen race strategy delivers maximum points with minimal risk. Teams adjust tactics based on:
- Tire wear and performance
- Fuel consumption and engine management
- Competitor pace and track position
- Safety car periods
Optimization Techniques
- Pit Stop Timing: Calculating the ideal laps for stops based on tire life and track position
- Tire Compound Usage: Using different compounds strategically to gain speed and durability
- Fuel and Engine Modes: Adjusting car settings for optimal performance during overtakes or defense
- Driver Adaptation: Real-time feedback to fine-tune driving style for tire conservation or aggression
Continuous Improvement
After each race, teams analyze data to refine strategies:
- Telemetry review for lap-by-lap performance
- Competitor behavior analysis
- Mistakes identification for future races
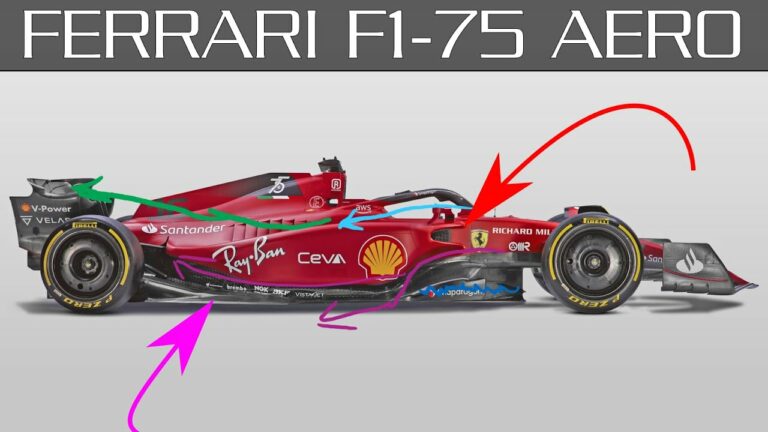
Continuous optimization ensures teams stay competitive throughout the season, with every aerodynamic tweak providing a crucial aerodynamics edge on the track.
Common Race Strategy Mistakes in F1
Even the best teams sometimes falter. Common mistakes include:
1. Poor Pit Stop Timing
Stopping too early or too late can cost positions, especially when tire performance drops rapidly.
2. Incorrect Tire Strategy
Choosing the wrong tire compound for track conditions can reduce grip and increase lap times, directly impacting Formula 1 racing dynamics and overall race strategy.
3. Ignoring Competitor Moves
Failing to anticipate rival strategies can result in lost positions or being trapped behind slower cars.
4. Overcomplicating the Plan
Complex strategies can be hard to execute; simpler, flexible strategies often perform better.
5. Underestimating External Factors
Weather, safety car periods, and mechanical failures can drastically alter outcomes if not considered.
Race Strategy Planning for F1 Teams
Pre-Race Planning
F1 teams prepare months in advance:
- Data Analysis: Studying past races and historical lap times
- Simulations: Testing multiple scenarios for pit stops, tire usage, and safety car impacts
- Strategy Meetings: Aligning engineers, drivers, and strategists
Live Race Adjustments
During the Grand Prix, race engineers continuously monitor:
- Tire degradation
- Gap to competitors
- Weather updates
- Safety car periods
This allows real-time strategy changes to optimize outcomes.
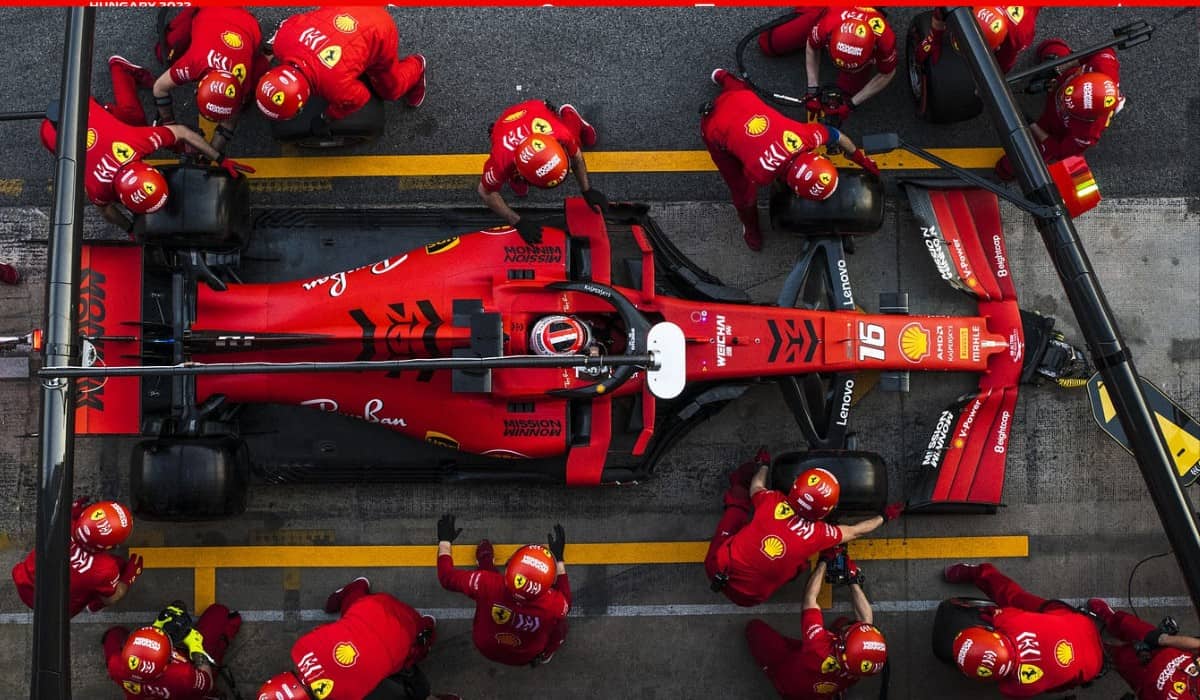
Pit Stop Execution
Pit stops are crucial. Teams plan:
- Pit lane entry and exit timing
- Tire compound changes
- Minimizing delay in traffic
- Coordination of lollipop or automated systems
Formula 1-Specific Strategy Considerations
DRS and Overtaking
Deployable DRS zones affect overtaking strategy, especially on circuits with long straights.
Qualifying Impact
Starting position significantly influences race strategy. Securing pole position gives a Formula 1 driver more flexibility in tire choices and pit stop planning, shaping the approach to the entire race.
Safety Car Strategy
Safety cars can change the race outcome instantly. Teams often plan alternate strategies to take advantage of safety car periods.
Weather Adaptation
Rain or changing conditions requires quick tire changes and strategy recalibration to maintain competitiveness.
Sim Racing and F1 Strategy Learning
Sim racing platforms like F1 23, iRacing, or Assetto Corsa allow enthusiasts to practice F1 strategies:
- Practice Sessions: Test tire and fuel management
- Simulated Races: Apply pit stop and DRS strategies
- Data Analysis: Refine race decision-making skills
Sim racing is an excellent way to understand F1 strategy without the high costs of real-world racing.
FAQ – Formula 1 Race Strategy
What is a Formula 1 race strategy?
It is a detailed plan used by F1 teams to maximize race performance, including tires, pit stops, fuel, and driver tactics.
Why is simulation important in F1 strategy?
Simulations predict race scenarios, optimize pit stops, and reduce risks without on-track testing.
How do F1 teams optimize race strategy?
By adjusting tire usage, pit timing, fuel and engine modes, and driver tactics for maximum efficiency and performance.
What are common mistakes in F1 race strategy?
Mistakes include poor pit timing, wrong tire choices, ignoring competitors, overcomplicated plans, and underestimating weather or safety cars.
How does safety car impact strategy?
Safety car periods can allow teams to pit with minimal time loss and adjust strategy based on track position.
Can sim racing help understand F1 strategy?
Yes, simulators allow players to practice pit stops, tire management, and strategic decision-making in a realistic environment.
How do tire rules affect F1 strategy?
FIA requires use of at least two dry tire compounds in a race, influencing pit stops and performance planning.